[ad_1]

National Insurance payments are being cut for millions of workers.
However, other changes mean the amount of tax people pay overall is rising to record levels.
How is National Insurance changing?
From 6 January, 27 million workers will pay 10% on earnings between £12,571 and £50,270. This replaces the previous National Insurance (NI) rate of 12%.
There are also two changes to NI coming for the UK’s two million self-employed people.
From 6 April 2024, they will pay 8% on profits between £12,571 and £50,270, down from 9%. The government says this will be worth £350 a year for self-employed people earning £28,200.
From the same date, self-employed people will no longer pay a separate category of NI called Class 2 contributions. The government says this will save the average self-employed person £192 a year.
NI on income and profits above £50,270 will remain at 2%.
It is not paid by people over state pension age, even if they are working. The rules apply across the UK.
What is happening to National Insurance thresholds?
NI is the second biggest source of money for the government.
It has frozen the level of income at which you start paying NI (the threshold) at £12,570 until 2028.
It means that as wages rise, more people will have to pay NI.
Why are millions paying more income tax?
As wages rise, more people will also have to start paying income tax and more people will have to pay higher rates.
The tax-free personal allowance will remain at £12,570. (Most taxpayers do not pay any tax on income below this level).
The point at which higher tax rates take effect will also not be increased.
The OBR says it means the tax burden is going up “to its highest level in the post-war era”.
What are the current rates of income tax?
You pay income tax to the government on earnings from employment and profits from self-employment.
These rates apply in England, Wales and Northern Ireland:
The basic rate of income tax is 20% and is paid on earnings between £12,571 and £50,270 during the tax year, which runs from 6 April to 5 April the following year.
The higher rate of income tax is 40%, and is paid on earnings between £50,271 and £125,140.
Once you earn more than £100,000 a year, you also start losing your tax-free personal allowance. This means you have to pay income tax of 40% on some of the first £12,570 of your earnings.
You lose £1 of your personal allowance for every £2 that your income goes above £100,000. So if you earn more than £125,140 a year, you no longer get any tax-free personal allowance.
The additional rate of income tax is 45%, and is paid on all earnings above £125,140 a year.
How is tax different in Scotland?
From April 2023 the rates are:
- Tax-free personal allowance: £12,570 (reduced by £1 for every £2 earned above £100,000)
- Starter rate of 19%: £12,571 to £14,732
- Scottish basic rate of 20%: £14,733 to £25,688
- Intermediate rate of 21%: £25,689 to £43,662
- Higher rate of 42%: £43,663 to £125,140
- Top rate of 47%: above £125,140
- Tax-free personal allowance: £12,570 (reduced by £1 for every £2 earned above £100,000)
- Starter rate of 19%: £12,571 to £14,876
- Scottish basic rate of 20%: £14,877 to £26,561
- Intermediate rate of 21%: £26,562 to £43,662
- Higher rate of 42%: £43,663 to £75,000
- Advanced rate of 45%: £75,001 to £125,140
- Top rate of 48%: above £125,140
The Scottish government estimates that 114,000 people will pay the new advanced tax rate and a further 40,000 the top rate.
Who pays most in income tax?
For most families, income tax is the single biggest tax.
But poorer households tend to pay more through indirect taxes on the money they spend.
For the poorest fifth of households, VAT is the biggest single tax paid.
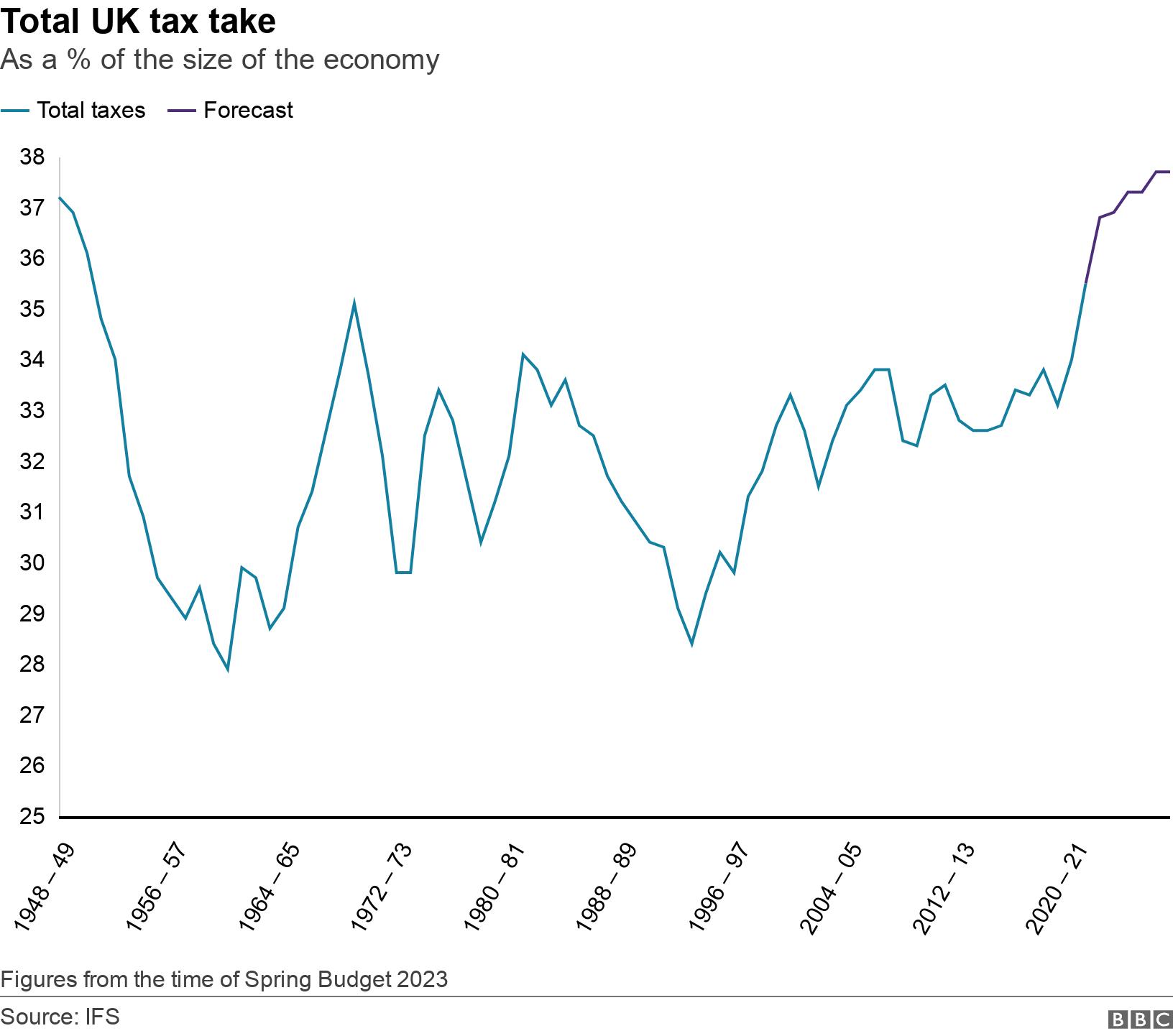
How high are UK taxes historically?
One way of measuring how high overall taxes are is to compare them with the size of the economy.
At the time of the Autumn Statement, the OBR said they would rise “in each of the next five years to a post-war high of 38% of GDP”.
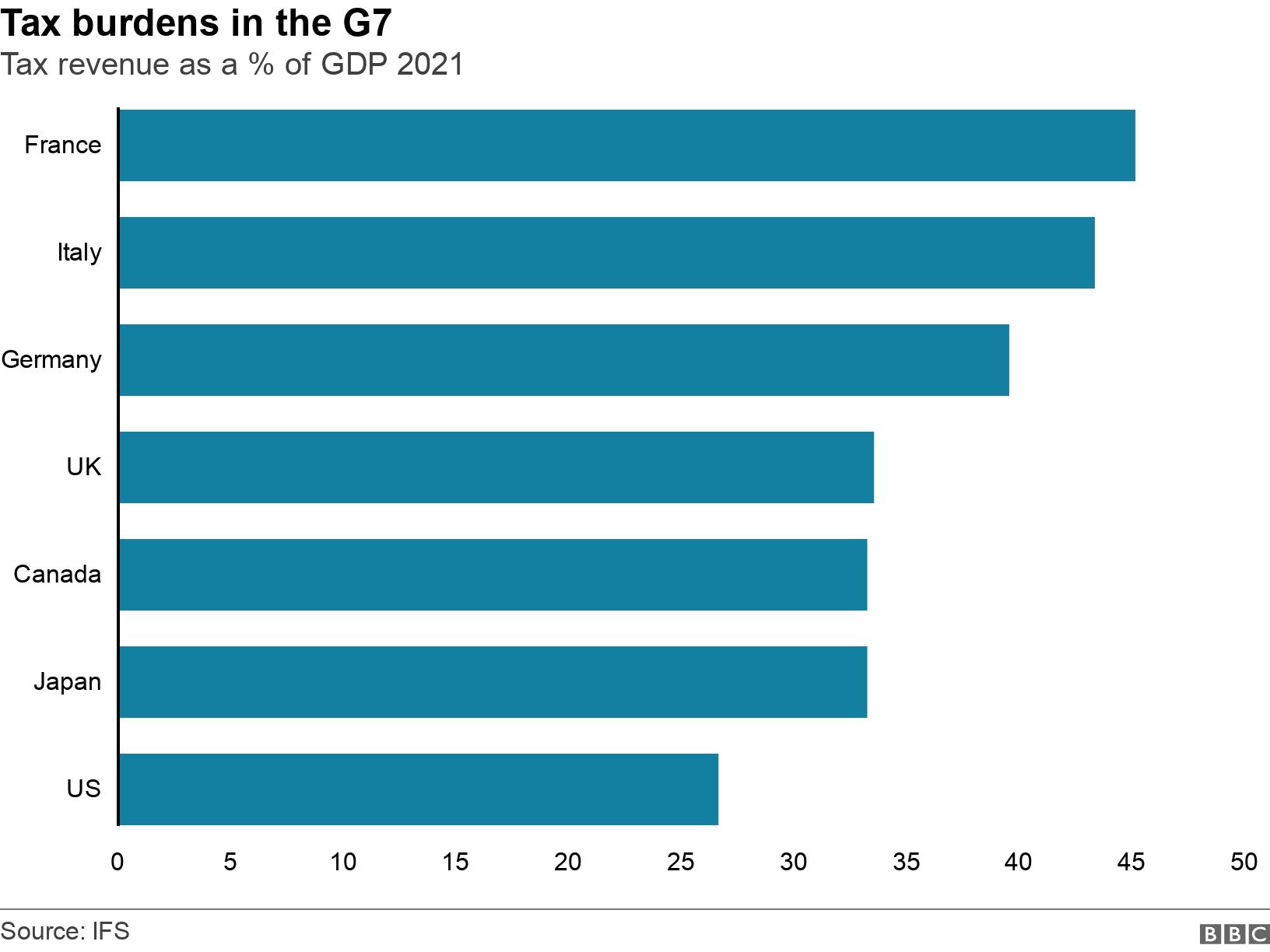
How do UK taxes compare with other countries?
If you look at the amount of tax raised as a proportion of the size of the economy in 2021 – the most recent year for which international comparisons can be made – the figure was 33.5%.
That puts the UK right in the middle of the G7 group of big economies.
France, Italy and Germany tax more, Canada, Japan and the US tax less.
[ad_2]
Source link


